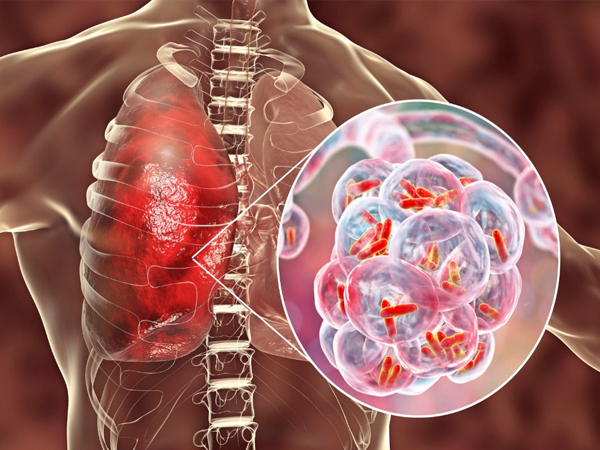
Tuberculosis - or TB, as it's commonly called - is a contagious infection that usually attacks the lungs. It can also spread to other parts of the body, like the brain and spine. A type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes it.
In the 20th century, TB was a leading cause of death in the United States. Today, most cases are cured with antibiotics. But it takes a long time. You have to take meds for at least 6 to 9 months.
Through the air, just like a cold or the flu. When someone who's sick coughs, sneezes, talks, laughs, or sings, tiny droplets that contain the germs are released. If you breathe in these nasty germs, you get infected.
TB is contagious, but it’s not easy to catch. The germs grow slowly. You usually have to spend a lot of time around a person who has it. That’s why it’s often spread among co-workers, friends, and family members.
Tuberculosis germs don’t thrive on surfaces. You can't get the disease from shaking hands with someone who has it, or by sharing their food or drink.
A TB infection doesn't mean you'll get sick. There are two forms of the disease:
Latent TB: You have the germs in your body, but your immune system stops them from spreading. That means you don't have any symptoms and you’re not contagious. But the infection is still alive in your body and can one day become active. If you are at high risk for re-activation — for instance, you have HIV, your primary infection was in the last 2 years, your chest X-ray is abnormal, or you are immunocompromised --- your doctor will treat you with antibiotics to lower the risk for developing active TB.
Active TB disease: This means the germs multiply and can make you sick. You can spread the disease to others. Ninety percent of adult cases of active TB are from the reactivation of a latent TB infection.