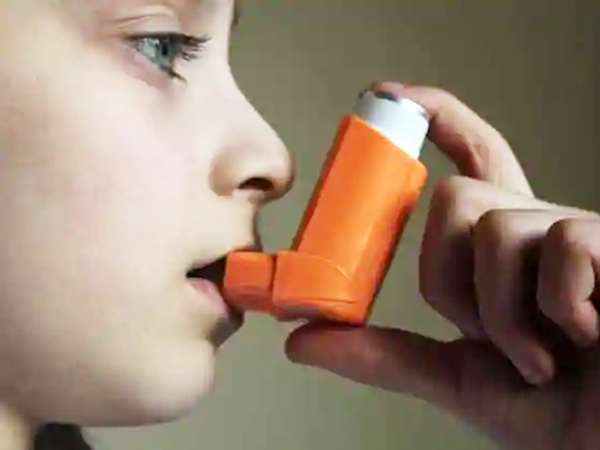
Asthma is a common long-term condition that can cause coughing, wheezing, chest tightness and breathlessness. Asthma is a chronic disease involving the airways in the lungs. These airways, or bronchial tubes, allow air to come in and out of the lungs.
Asthma is caused by inflammation of the small tubes, called bronchi, which carry air in and out of the lungs. If you have asthma, the bronchi will be inflamed and more sensitive than normal.
While there is no cure for asthma, but once it is properly diagnosed and a treatment plan is in place you will be able to manage your condition, and your quality of life will improve. There are a number of treatments that can help control the condition.
Treatment is based on two important goals, which are:
For most people, this will involve the occasional – or, more commonly, daily – use of medications, usually taken using an inhaler. However, identifying and avoiding possible triggers is also important. You should have a personal asthma action plan agreed with your doctor or nurse that includes information about the medicines you need to take, how to recognise when your symptoms are getting worse, and what steps to take when they do so.